Problem description
Given an undirected graph, a dominating set is a subset of its nodes such that any node can be connected by an edge to a node of this subset. In this example, we consider the problem of finding a minimum size dominating set such that the induced subgraph is connected. The code generating the input graph is given below: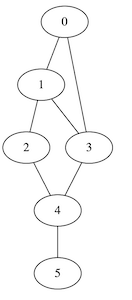
Input graph
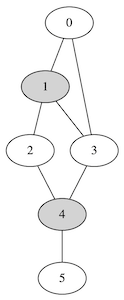
Disconnected minimum dominating set
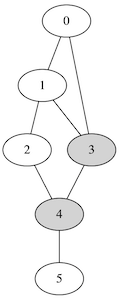
Connected minimum dominating set
/**
* Creates an undirected graph of 6 nodes and 7 edges
* @return an UndirectedGraph
*/
private static UndirectedGraph createInputGraph() {
// creates a graph with 6 nodes (from 0 to 5)
UndirectedGraph inputGraph = new UndirectedGraph(6, SetType.BITSET, true);
// add 7 edges
int[][] edges = {{0, 1}, {1, 2}, {0, 3}, {1, 3}, {2, 4}, {3, 4}, {4, 5}};
Arrays.stream(edges).forEach(edge -> inputGraph.addEdge(edge[0], edge[1]));
return inputGraph;
}
UndirectedGraph inputGraph = createInputGraph();
System.out.println("input graph compact representation: \n" + inputGraph);
System.out.println("input graph graphviz representation:\n" + inputGraph.graphVizExport());
Modelling this problem
Creating a graph variable
Let's now model this problem using Choco Solver. A graph variable is created to represent the search of a subgraph of the given input graph. To do so, two bounds are defined. The graph lower bound: an empty graph ; and the graph upper bound: the input graph. Any value of the variable should be included between those two bounds.
/**
* Create a graph variable representing an induced subgraph of inputGraph
* @param model a choco-solver Model
* @param inputGraph an undirected graph defining the variable's upper bound
* @return an UndirectedGraphVar
*/
private static UndirectedGraphVar createGraphVariable(Model model, UndirectedGraph inputGraph) {
int n = inputGraph.getNbMaxNodes();
// --- graph lower bound : an empty graph
UndirectedGraph GLB = new UndirectedGraph(model, n, SetType.BITSET, false);
UndirectedGraph GUB = new UndirectedGraph(model, n, SetType.BITSET, false);
for (int i : inputGraph.getNodes()) {
GUB.addNode(i); // all nodes are possible
for (int j : inputGraph.getNeighborsOf(i)) {
GUB.addEdge(i, j); // all edges of inputGraph are possible
}
}
// create a graph variable with domain [GLB, GUB]
// any of its value will be a supergraph of GLB and a subgraph of GUB
return model.graphVar("g", GLB, GUB);
}
Connectivity constraint
The connectivity constraint is ensured by a dedicated global constraint, named connected. This constraint incorporates efficient graph algorithms and avoids costly reformulation.
// --- Connectivity constraint : the graph variable must be connected
model.connected(subgraph).post();
Boolean representation of graph nodes
To simplify the rest of the modeling, we introduce a dual representation, based on Boolean variables.
// DOMINATING SET
// --- one boolean variable per node
BoolVar[] domSet = model.boolVarArray(n);
model.nodesChanneling(subgraph, domSet).post();
Each node of the graph is thus connected to a binary variable. Since the actual decision variables are the graph nodes, not its edges, it will be more convenient to branch on the binary variables. The graph variable then becomes nothing more than a support for the global connectivity constraint but no longer constitutes a decision variable: it is not necessary to branch on the graph's arcs.
Covering constraints
The coverage constraints are expressed using logical constraints (OR) on Boolean variables.
// --- covering constraints
// (each node should be either dominating or a direct neighbor of a dominating node)
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int idx = 0;
BoolVar[] cluster = new BoolVar[1 + inputGraph.getNeighborsOf(i).size()];
cluster[idx++] = domSet[i];
for (int j : inputGraph.getNeighborsOf(i)) {
cluster[idx++] = domSet[j];
}
model.or(cluster).post();
}
Minimizing the cardinality of the dominating set
The objective function consists of minimizing the number of nodes, which is the sum of the binary variables associated with the graph nodes. It is also possible to use the nbNodes constraint.
// --- minimize the number of nodes in the dominating set
IntVar size = model.sum("nbNodes", domSet);
model.setObjective(Model.MINIMIZE, size);
Solving this problem
Search heuristic
We can specify a search heuristic removing nodes with low degree first. This should provide a good initial solution. Therefore, we sort the binary variables in ascending order based on the number of neighbors in the input graph. The value selection involves choosing the lower bound, which corresponds to removing nodes from the graph.
// --- sort nodes by increasing neighborhood size
BoolVar[] orderedDomVar = IntStream.range(0, n)
.boxed()
.sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(i -> inputGraph.getNeighborsOf(i).size()))
.map(i -> domSet[i])
.toArray(BoolVar[]::new);
model.getSolver().setSearch(Search.inputOrderLBSearch(orderedDomVar));
Calling the solver
Once the constraints and objective function are set, the search for improving solutions can be invoked using the solver's solve method. Here, the first solution is optimal.
// SOLVING
System.out.println("start solving...");
while (model.getSolver().solve()) {
int[] solution = IntStream.range(0, n).filter(i -> domSet[i].isInstantiatedTo(1)).toArray();
System.out.println("dominating set : " + Arrays.toString(solution));
}
Console output:
input graph compact representation:
nodes :
[0,5]
neighbors :
0 -> {1 3 }
1 -> {0 2 3 }
2 -> {1 4 }
3 -> {0 1 4 }
4 -> {2 3 5 }
5 -> {4 }
input graph graphviz representation:
graph G{
0 1 2 3 4 5 ;
0 -- 1 ;
0 -- 3 ;
1 -- 2 ;
1 -- 3 ;
2 -- 4 ;
3 -- 4 ;
4 -- 5 ;
}
start solving...
dominating set : [3, 4]
Model[Model-0], 1 Solutions, MINIMIZE nbNodes = 2, Resolution time 0,023s, Time to best solution 0,002s, 5 Nodes (213,0 n/s), 0 Backtracks, 0 Backjumps, 0 Fails, 0 Restarts
** Choco 4.10.14 (2023-11) : Constraint Programming Solver, Copyright (c) 2010-2023
- Model[Model-0] features:
Variables : 14
Constraints : 15
Building time : 0,047s
User-defined search strategy : yes
Complementary search strategy : no
- Complete search - 1 solution found.
Model[Model-0]
Solutions: 1
MINIMIZE nbNodes = 2,
Building time : 0,047s
Resolution time : 0,028s
Time to best solution : 0,002s
Nodes: 5 (180,5 n/s)
Backtracks: 9
Backjumps: 0
Fails: 4
Restarts: 0
Complete code
/*
* Copyright (C) 2025 COSLING S.A.S.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package com.cosling.tutorials;
import org.chocosolver.solver.Model;
import org.chocosolver.solver.search.strategy.Search;
import org.chocosolver.solver.variables.BoolVar;
import org.chocosolver.solver.variables.IntVar;
import org.chocosolver.solver.variables.UndirectedGraphVar;
import org.chocosolver.util.objects.graphs.UndirectedGraph;
import org.chocosolver.util.objects.setDataStructures.SetType;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
/**
* Simple example of connected dominating set problem
* Shows how to use graph-set channeling and how to create a set constraint
* @author Jean-Guillaume FAGES (cosling)
* @version Choco Solver 4.10.14
*/
public class DomSetProblem {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// INPUT GRAPH --- Generation
UndirectedGraph inputGraph = createInputGraph();
int n = inputGraph.getNbMaxNodes(); // number of nodes
// print input graph as graphviz format to display it on http://www.webgraphviz.com/
System.out.println("input graph compact representation: \n" + inputGraph);
System.out.println("input graph graphviz representation:\n"
+ inputGraph.graphVizExport());
Model model = new Model();
// GRAPH VARIABLE : initial domain (from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dominating_set)
UndirectedGraphVar subgraph = createGraphVariable(model, inputGraph);
// --- Connectivity constraint : the graph variable must be connected
model.connected(subgraph).post();
// DOMINATING SET
// --- one boolean variable per node
BoolVar[] domSet = model.boolVarArray(n);
model.nodesChanneling(subgraph, domSet).post();
// --- minimize the number of nodes in the dominating set
IntVar size = model.sum("nbNodes", domSet);
model.setObjective(Model.MINIMIZE, size);
// --- covering constraints
// (each node should be either dominating or a direct neighbor of a dominating node)
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int idx = 0;
BoolVar[] cluster = new BoolVar[1 + inputGraph.getNeighborsOf(i).size()];
cluster[idx++] = domSet[i];
for (int j : inputGraph.getNeighborsOf(i)) {
cluster[idx++] = domSet[j];
}
model.or(cluster).post();
}
// SEARCH
// --- sort nodes by increasing neighborhood size
BoolVar[] orderedDomVar = IntStream.range(0, n)
.boxed()
.sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(i -> inputGraph.getNeighborsOf(i).size()))
.map(i -> domSet[i])
.toArray(BoolVar[]::new);
model.getSolver().setSearch(Search.inputOrderLBSearch(orderedDomVar));
// SOLVING
System.out.println("start solving...");
while (model.getSolver().solve()) {
int[] solution = IntStream.range(0, n).filter(i -> domSet[i].isInstantiatedTo(1)).toArray();
System.out.println("dominating set : " + Arrays.toString(solution));
System.out.println(model.getSolver().toOneLineString());
}
model.getSolver().printStatistics();
}
/**
* Creates an undirected graph of 6 nodes and 7 edges
*
* @return an UndirectedGraph
*/
private static UndirectedGraph createInputGraph() {
// creates a graph with 6 nodes (from 0 to 5)
UndirectedGraph inputGraph = new UndirectedGraph(6, SetType.BITSET, true);
// add 7 edges
int[][] edges = {{0, 1}, {1, 2}, {0, 3}, {1, 3}, {2, 4}, {3, 4}, {4, 5}};
Arrays.stream(edges).forEach(edge -> inputGraph.addEdge(edge[0], edge[1]));
return inputGraph;
}
/**
* Create a graph variable representing an induced subgraph of inputGraph
*
* @param model a choco-solver Model
* @param inputGraph an undirected graph defining the variable's upper bound
* @return an UndirectedGraphVar
*/
private static UndirectedGraphVar createGraphVariable(Model model, UndirectedGraph inputGraph) {
int n = inputGraph.getNbMaxNodes();
// --- graph lower bound : an empty graph
UndirectedGraph GLB = new UndirectedGraph(model, n, SetType.BITSET, false);
UndirectedGraph GUB = new UndirectedGraph(model, n, SetType.BITSET, false);
for (int i : inputGraph.getNodes()) {
GUB.addNode(i); // all nodes are possible
for (int j : inputGraph.getNeighborsOf(i)) {
GUB.addEdge(i, j); // all edges of inputGraph are possible
}
}
// create a graph variable with domain [GLB, GUB]
// any of its value will be a supergraph of GLB and a subgraph of GUB
return model.graphVar("g", GLB, GUB);
}
}