Description du problème
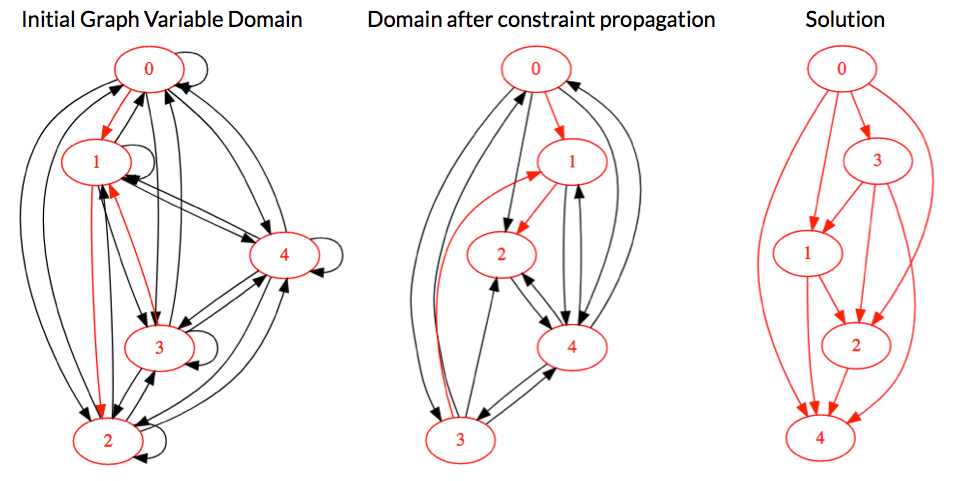
Dans cet exemple, nous modélisons et résolvons un problème de recherche d'un graphe orienté sans circuits (DAG) en Programmation Par Contraintes. Pour cela, nous utilisons le module de graphes de Choco Solver pour créer une variable graphe ainsi que des contraintes de graphe. Remarquez que depuis Choco Graph 4.2.0, les variables graphes peuvent exporter leur domaine au format de Graphviz.Modélisation du problème
/*
* Copyright (C) 2017 COSLING S.A.S.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
import org.chocosolver.graphsolver.GraphModel;
import org.chocosolver.graphsolver.variables.DirectedGraphVar;
import org.chocosolver.solver.exception.ContradictionException;
import org.chocosolver.solver.variables.IntVar;
import org.chocosolver.util.objects.graphs.DirectedGraph;
import org.chocosolver.util.objects.setDataStructures.SetType;
/**
* Example of Graph Variable in Choco Solver: computes a directed acyclic graph
* @author Jean-Guillaume FAGES (cosling)
* @version choco-solver-4.0.4
* @version choco-graph-4.2.0
*/
public class DAG {
public static void main(String[] args){
int n = 5;
GraphModel model = new GraphModel();
// VARIABLE COUNTING THE NUMBER OF ARCS
IntVar nbArcs = model.intVar("arcCount", 0, n * n, true);
// GRAPH VARIABLE : initial domain (every node belongs to the solution)
DirectedGraph GLB = new DirectedGraph(model, n, SetType.BITSET, true);
DirectedGraph GUB = new DirectedGraph(model, n, SetType.BITSET, true);
GLB.addArc(0,1); // some arbitrary mandatory arcs
GLB.addArc(1,2);
GLB.addArc(3,1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
GUB.addArc(i, j); // potential edge
}
}
DirectedGraphVar dag = model.digraphVar("dag", GLB, GUB);
// CONSTRAINTS
model.noCircuit(dag).post();
model.nbArcs(dag, nbArcs).post();
// SOLVING AND PRINTS
System.out.println(dag.graphVizExport()); // displays initial graph domain
try {
model.getSolver().propagate(); // propagates constraints (without branching)
} catch (ContradictionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(dag.graphVizExport()); // displays graph domain after propagation
if (model.getSolver().solve()){
System.out.println("solution found : "+nbArcs);
System.out.println(dag.graphVizExport()); // displays solution graph
}
model.getSolver().printStatistics();
}
}
Résolution du problème
Le domaine de la variable de graphe avant et après propagation, ainsi que dans la solution trouvée, affiché grâce à webgraphviz: